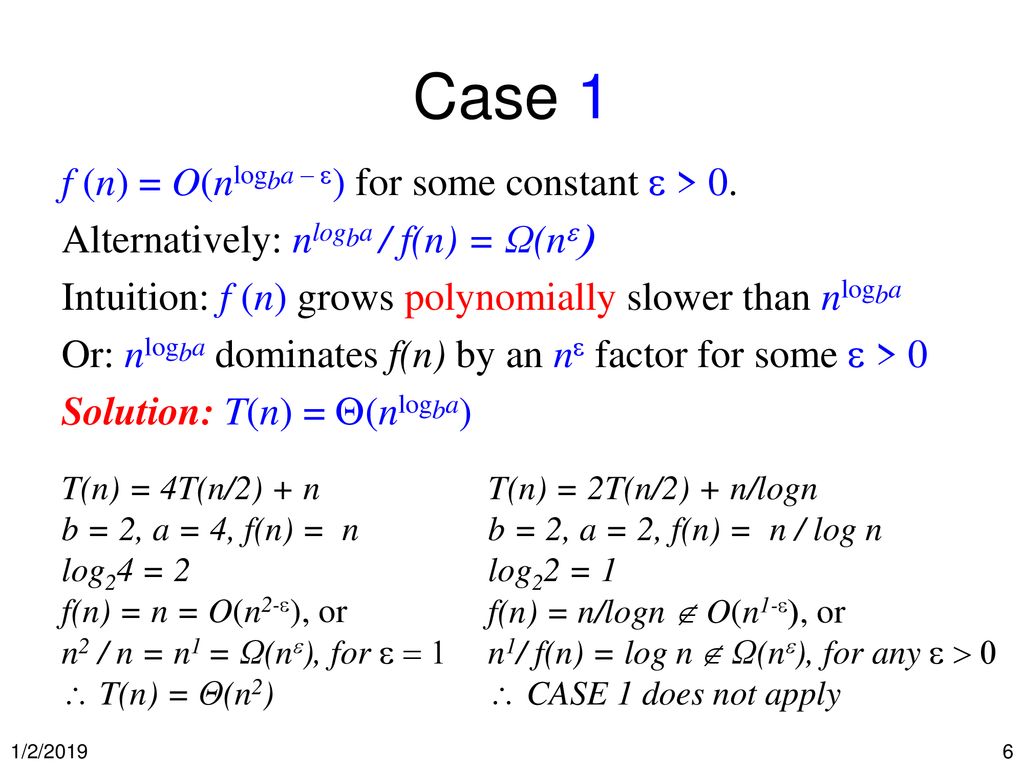
Master Theorem: T(n) = 2T (n/2) + n/log n = ? I thought the answer would be Θ (nlogn), but the solution says the Master Theorem does not apply. - Quora
T(n) = 3 * T (n / 2) + n * log(n), by using master theorem, which case should be applied here? - Quora

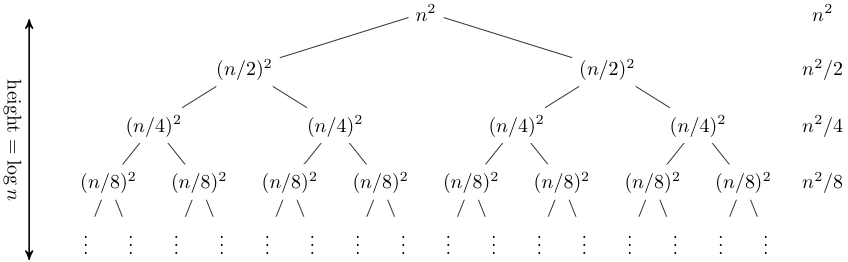
Solving Recurrence Relations T(n)= 2T(n/2)+n = 2*(2T(n/4)+n/2)+n = 4*T(n/4) +2*n = 8*T(n/8) + 3*n = 2 (log n) * T(1) + (log n) * n = n * 1 + n log